8556. Chain
Given a sequence of n integers
a1, a2,
..., an. For any element ak (k = 1, 2, ..., n) we find the first larger than ak element,
which is placed to the right of ak (if such exists).
Denote it by ak1. Then do the same with ak1 and denote the found element by ak2, and so on until we run out of the given
sequence. Thus formed subsequence ak1, ak2, ..., we call chain beginning at index k.
Write a program that outputs for any index k the length of the corresponding chain that starts at
index k.
Input. The first line contains positive integer n (0 < n ≤ 500000). The second line contains the elements of the given sequence a1, a2,
..., an (0 < ai < 106).
Output. Print in one line the sequence of chain’s lengths, corresponding to the
elements of the input data.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
10 3 2 4 2 11 2 7 5 8 10 |
2 2 1 1 0 3 2 2 1 0 |
SOLUTION
stack
Algorithm analysis
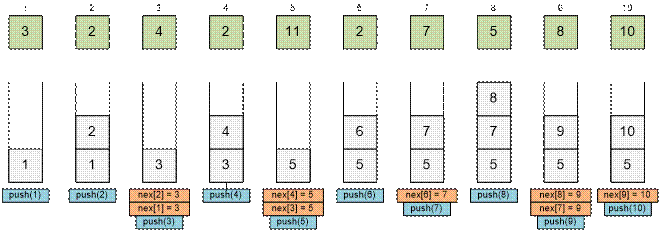
Declare an array nex such that nex[i] contains the index of the closest to the right element greater
than ai. For example, nex[i] = 0 means that there are no elements
to the right of ai greater
than ai.
Declare a stack s
that will store indices i instead
of numbers ai. Push the first item onto the stack: s.push (1) – push the index of the first item. Process sequentially the rest of the sequence numbers.
Let the current element be aj.
Then:
·
if a[s.top()]
≥ a[j], push index j into the stack: s.push(j);
·
otherwise,
until the stack is not empty and a[s.top()] < a[j], pop element from the stack i = s.top() and
set nex[i] = j. Upon completion of the loop push j into the stack: s.push(j);
Now, from
the nex array, the resulting sequence dp should be reconstructed, where dp[i] equals to the length of the chain starting from index i.
·
if nex[i] = 0, then dp[i] = 0;
·
otherwise dp[i] = dp[nex[i]] + 1;
Example
Fill the array dp from
right to left.
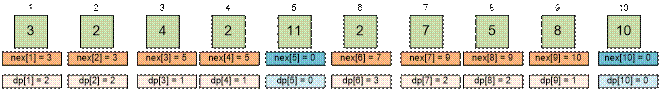
Algorithm
realization
Declare the arrays.
#define MAX 500001
int a[MAX], nex[MAX], dp[MAX];
stack<int> s;
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
Push to the stack the index of the first element – one.
s.push(1);
Sequentially
process the rest of the elements.
for(j = 2; j <= n; j++)
{
while(!s.empty())
{
i = s.top();
if(a[i] >= a[j]) break;
nex[i] = j;
s.pop();
}
s.push(j);
}
Recalculate
the resulting array.
dp[n] = 0;
for(i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
if (nex[i] == 0) dp[i] = 0;
else dp[i] = 1 + dp[nex[i]];
Print the
answer – the lengths of the chains
starting from position i.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d
",dp[i]);
printf("\n");
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[n+1];
int next[] = new int[n+1];
int dp[] = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
a[i] = con.nextInt();
Stack<Integer> s = new
Stack<Integer>();
s.push(1);
for(int j = 2; j <= n; j++)
{
while(!s.empty())
{
int i = s.peek();
if(a[i] >= a[j]) break;
next[i] = j;
s.pop();
}
s.push(j);
}
dp[n] = 0;
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
if (next[i] == 0) dp[i] = 0;
else dp[i] = 1 + dp[next[i]];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
System.out.print(dp[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}